8. Troubleshooting, FAQ, and Special Cases
This section presents some general troubleshooting tips outlining things to check to make sure the pipeline scripts will run smoothly. There are also some FAQ, and some guidance on special cases and how to handle them.
Note that this section is a work in progress and will continue to be updated as the pipeline is further developed and tested.
Troubleshooting: some general tips
- When running data cleaning (any stage), pay very close attention to the output on your screen. It tells you when everything runs smoothly, and if something goes wrong, in most cases it will be informative as to why and whereabouts things went wrong.
- Avoid having extra white space in your INI file between
[TRACE]and[END]. Each parameter must be defined on a new line, with no wraparound. We recommend using a text editor that has line numbers (such as VS Code) to help you avoid and/or diagnose this issue. - If you downloaded the Biomet.net library (rather than cloned it), make sure that you renamed it
Biomet.netsince the download includes “main” in the folder name.
FAQ
I have multiple files containing data from one site, e.g., daily, monthly, or annual files. How do I create one database from all my files?
- See section …
I have multiple flux sites. Once I’ve added one site and created my database with data from that site (and cleaned it, etc.), what are the steps to move on to my next site?
- See section …
How do I incorporate data from other sources such as nearby climate stations, e.g., for gap-filling, into my database?
- See section …
When I run the third stage cleaning, why does it finish so quickly (less than a minute), and/or why is there is no data output in the
Databasedirectory?Check the log file that is produced automatically when running the third stage (
SITEID1_ThirdStageCleaning.log). It is informative and will usually tell you the issue; it is located here: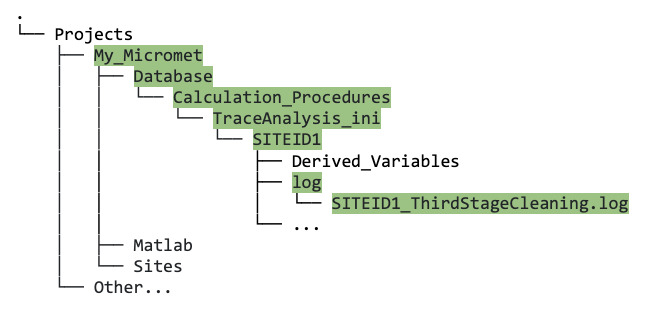
Screenshot showing the location of the third stage log file.
Check that all R packages are installed and loaded. Refer to the code provided in section 2.5 for this.
Check that after you downloaded and unzipped the
Biomet.netlibrary, you renamed it fromBiomet.net-maintoBiomet.net.
Special Cases
This section outlines some recurring special cases and how to deal with them:
There is a variable defined in an include INI file that I have no raw input data for.
In this case, you can add the following code to the global variables section of your first stage INI file. Remember to change the name of the “dummyVariable” to match the name of the variable you do not have.
%-->Avoiding errors due to missing input files dateRangeNoData = [datenum(1900,1,1) datenum(1900,12,31)] globalVars.Trace.dummyVariable.inputFileName_dates = dateRangeNoData
E.g., if you are running data cleaning for the year 2023, this code essentially tells the pipeline that for this “dummyVariable”, no data exists for 2023 (and only exists for the year 1900), and the program will continue smoothly with no errors.
I am using an earlier version of Matlab than 2023b, and I’m getting an error when running the
create_TAB_ProjectFoldersfunction. How do I fix this?Download this zip file, unzip, and put the contents of the unzipped directory within your own project directory; make sure your directory structure looks like figure 4.1 in section 4.
The
gitclonefunction is used within thecreate_TAB_ProjectFoldersfunction to transfer (clone) the directory structure and files within. However,gitclonewas only added to Matlab 2023b, so you need to download this project directory structure directly.If it is an error related to
gitclone, the error will occur on the line that gitclone is called, so you can check this in the error message, e.g., it may look like this:Error: File: create_TAB_ProjectFolders.m Line: 66 Column: 32 Incorrect use of '=' operator. To assign a value to a variable, use '='. To compare values for equality, use '=='.